| dc.contributor.author | Mühlen, Jan M. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Stang, Julie | |
| dc.contributor.author | Júdice, Pedro B. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Molina-Garcia, Pablo | |
| dc.contributor.author | Johnston, William | |
| dc.contributor.author | Sardinha, Luís B. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Ortega, Francisco B. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Caulfield, Brian | |
| dc.contributor.author | Bloch, Wilhelm | |
| dc.contributor.author | Cheng, Sulin | |
| dc.contributor.author | Ekelund, Ulf | |
| dc.contributor.author | Brønd, Jan Christian | |
| dc.contributor.author | Grøntved, Anders | |
| dc.contributor.author | Schumann, Moritz | |
| dc.contributor.author | Skovgaard, Esben Lykke | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2021-12-10T09:48:25Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2021-12-10T09:48:25Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2021-04-06T13:37:20Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2021 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2021, 55(14), 767-779. | en_US |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0306-3674 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11250/2833733 | |
| dc.description | This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. | en_US |
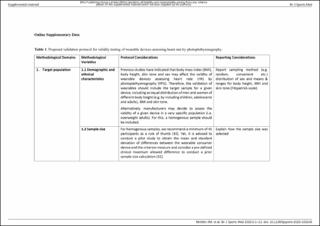
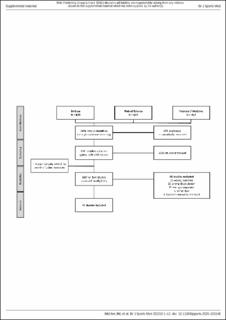
| dc.description.abstract | Assessing vital signs such as heart rate (HR) by wearable devices in a lifestyle-related environment provides widespread opportunities for public health related research and applications. Commonly, consumer wearable devices assessing HR are based on photoplethysmography (PPG), where HR is determined by absorption and reflection of emitted light by the blood. However, methodological differences and shortcomings in the validation process hamper the comparability of the validity of various wearable devices assessing HR. Towards Intelligent Health and Well-Being: Network of Physical Activity Assessment (INTERLIVE) is a joint European initiative of six universities and one industrial partner. The consortium was founded in 2019 and strives towards developing best-practice recommendations for evaluating the validity of consumer wearables and smartphones. This expert statement presents a best-practice validation protocol for consumer wearables assessing HR by PPG. The recommendations were developed through the following multi-stage process: (1) a systematic literature review based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, (2) an unstructured review of the wider literature pertaining to factors that may introduce bias during the validation of these devices and (3) evidence-informed expert opinions of the INTERLIVE Network. A total of 44 articles were deemed eligible and retrieved through our systematic literature review. Based on these studies, a wider literature review and our evidence-informed expert opinions, we propose a validation framework with standardised recommendations using six domains: considerations for the target population, criterion measure, index measure, testing conditions, data processing and the statistical analysis. As such, this paper presents recommendations to standardise the validity testing and reporting of PPG-based HR wearables used by consumers. Moreover, checklists are provided to guide the validation protocol development and reporting. This will ensure that manufacturers, consumers, healthcare providers and researchers use wearables safely and to its full potential. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | en_US |
| dc.subject | cardiology | en_US |
| dc.subject | consensus statement | en_US |
| dc.subject | public health | en_US |
| dc.subject | sports and exercise medicine | en_US |
| dc.subject | sports medicine | en_US |
| dc.title | Recommendations for determining the validity of consumer wearable heart rate devices: Expert statement and checklist of the INTERLIVE Network | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | en_US |
| dc.type | Journal article | en_US |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021 | en_US |
| dc.source.pagenumber | 767-779 | en_US |
| dc.source.volume | 55 | en_US |
| dc.source.journal | British Journal of Sports Medicine | en_US |
| dc.source.issue | 14 | en_US |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1136/bjsports-2020-103148 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 1902401 | |
| dc.description.localcode | Institutt for idrettsmedisinske fag / Department of Sports Medicine | en_US |
| cristin.ispublished | true | |
| cristin.fulltext | original | |
| cristin.qualitycode | 2 | |