| dc.contributor.author | Fairclough, Stuart J. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Hurter, Liezel | |
| dc.contributor.author | Dumuid, Dorothea | |
| dc.contributor.author | Gába, Ales | |
| dc.contributor.author | Rowlands, Alex V. | |
| dc.contributor.author | del Pozo Cruz, Borja | |
| dc.contributor.author | Cox, Ashley | |
| dc.contributor.author | Crotti, Matteo | |
| dc.contributor.author | Foweather, Lawrence | |
| dc.contributor.author | Jones, Owen R. | |
| dc.contributor.author | McCann, Debroah A. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Noonan, Robert J. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Owen, Michael B. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Rudd, James Robert | |
| dc.contributor.author | Taylor, Sarah L | |
| dc.contributor.author | Tyler, Richard | |
| dc.contributor.author | Boddy, Lynne M | |
| dc.contributor.author | Graves, Lee E. F. | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2022-12-01T12:55:40Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2022-12-01T12:55:40Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2022-10-19T11:08:07Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2022 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022, 19(14), Artikkel 8778. | en_US |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1661-7827 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3035375 | |
| dc.description | This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). | en_US |
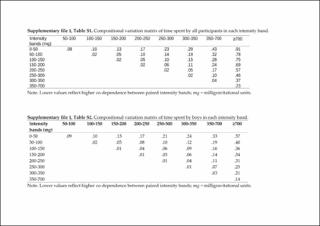
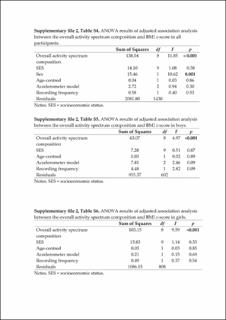
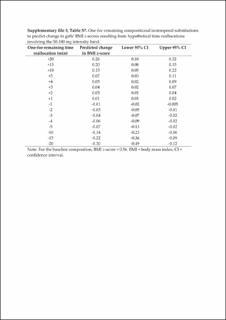
| dc.description.abstract | We examined the compositional associations between the intensity spectrum derived from incremental acceleration intensity bands and the body mass index (BMI) z-score in youth, and investigated the estimated differences in BMI z-score following time reallocations between intensity bands. School-aged youth from 63 schools wore wrist accelerometers, and data of 1453 participants (57.5% girls) were analysed. Nine acceleration intensity bands (range: 0–50 mg to ≥700 mg) were used to generate time-use compositions. Multivariate regression assessed the associations between intensity band compositions and BMI z-scores. Compositional isotemporal substitution estimated the differences in BMI z-score following time reallocations between intensity bands. The ≥700 mg intensity bandwas strongly and inversely associated with BMI z-score (p < 0.001). The estimated differences in BMI z-score when 5 min were reallocated to and from the ≥700 mg band and reallocated equally among the remaining bands were −0.28 and 0.44, respectively (boys), and −0.39 and 1.06, respectively (girls). The time in the ≥700 mg intensity band was significantly associated with BMI z-score, irrespective of sex. When even modest durations of time in this band were reallocated, the asymmetrical estimated differences in BMI z-score were clinically meaningful. The findings highlight the utility of the full physical activity intensity spectrum over a priori-determined absolute intensity cut-point approaches. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | en_US |
| dc.subject | accelerometer | en_US |
| dc.subject | adiposity | en_US |
| dc.subject | adolescents | en_US |
| dc.subject | children | en_US |
| dc.subject | CoDa | en_US |
| dc.subject | intensity spectrum | en_US |
| dc.subject | physical activity | en_US |
| dc.title | The physical behaviour intensity spectrum and body mass index in school-aged youth: A compositional analysis of pooled individual participant data | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | en_US |
| dc.type | Journal article | en_US |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | © 2022 by the authors | en_US |
| dc.source.pagenumber | 15 | en_US |
| dc.source.volume | 19 | en_US |
| dc.source.journal | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | en_US |
| dc.source.issue | 14 | en_US |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.3390/ijerph19148778 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 2062690 | |
| dc.description.localcode | Institutt for lærerutdanning og friluftslivsstudier / Department of Teacher Education and Outdoor Studies | en_US |
| dc.source.articlenumber | 8778 | en_US |
| cristin.ispublished | true | |
| cristin.fulltext | original | |
| cristin.qualitycode | 1 | |