| dc.contributor.author | Kulseng, Carl Petter Skaar | |
| dc.contributor.author | Nainamalai, Varatharajan | |
| dc.contributor.author | Grøvik, Endre | |
| dc.contributor.author | Årøen, Asbjørn | |
| dc.contributor.author | Geitung, Jonn Terje | |
| dc.contributor.author | Gjesdal, Kjell-Inge | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2023-05-03T18:44:50Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2023-05-03T18:44:50Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2023-01-19T10:32:55Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2023 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 24(2023), Artikkel 41. | en_US |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1471-2474 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3066059 | |
| dc.description | This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. | en_US |
| dc.description.abstract | Background: To study deep learning segmentation of knee anatomy with 13 anatomical classes by using a magnetic resonance (MR) protocol of four three-dimensional (3D) pulse sequences, and evaluate possible clinical usefulness.
Methods: The sample selection involved 40 healthy right knee volumes from adult participants. Further, a recently injured single left knee with previous known ACL reconstruction was included as a test subject. The MR protocol consisted of the following 3D pulse sequences: T1 TSE, PD TSE, PD FS TSE, and Angio GE. The DenseVNet neural network was considered for these experiments. Five input combinations of sequences (i) T1, (ii) T1 and FS, (iii) PD and FS, (iv) T1, PD, and FS and (v) T1, PD, FS and Angio were trained using the deep learning algorithm. The Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), Jaccard index and Hausdorff were used to compare the performance of the networks.
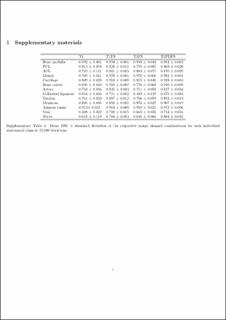
Results: Combining all sequences collectively performed significantly better than other alternatives. The following DSCs (±standard deviation) were obtained for the test dataset: Bone medulla 0.997 (±0.002), PCL 0.973 (±0.015), ACL 0.964 (±0.022), muscle 0.998 (±0.001), cartilage 0.966 (±0.018), bone cortex 0.980 (±0.010), arteries 0.943 (±0.038), collateral ligaments 0.919 (± 0.069), tendons 0.982 (±0.005), meniscus 0.955 (±0.032), adipose tissue 0.998 (±0.001), veins 0.980 (±0.010) and nerves 0.921 (±0.071). The deep learning network correctly identified the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear of the left knee, thus indicating a future aid to orthopaedics.
Conclusions: The convolutional neural network proves highly capable of correctly labeling all anatomical structures of the knee joint when applied to 3D MR sequences. We have demonstrated that this deep learning model is capable of automatized segmentation that may give 3D models and discover pathology. Both useful for a preoperative evaluation. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | en_US |
| dc.relation.uri | https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-023-06153-y | |
| dc.subject | deep learning | en_US |
| dc.subject | knee images segmentation | en_US |
| dc.subject | Magnetic Resonance Imaging | en_US |
| dc.subject | musculoskeletal | en_US |
| dc.subject | visualization | en_US |
| dc.title | Automatic segmentation of human knee anatomy by a convolutional neural network applying a 3D MRI protocol | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | en_US |
| dc.type | Journal article | en_US |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | © The Author(s) 2023 | en_US |
| dc.source.pagenumber | 12 | en_US |
| dc.source.volume | 24 | en_US |
| dc.source.journal | BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders | en_US |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1186/s12891-023-06153-y | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 2110064 | |
| dc.description.localcode | Institutt for idrettsmedisinske fag / Department of Sports Medicine | en_US |
| dc.source.articlenumber | 41 | en_US |
| cristin.ispublished | true | |
| cristin.fulltext | original | |
| cristin.qualitycode | 1 | |